How Do Cigarettes Affect The Body?
How do cigarettes affect the body? According to the World Health Organization (WHO), smoking kills more than 8 million people globally each year. Over 7 million of these deaths are due to direct tobacco use, while around 1.2 million people die from exposure to secondhand smoke.
Why is smoking so harmful?
Cigarette smoke contains 7,000 chemicals, of which 69 are carcinogenic. When you smoke, all these substances enter your body, attacking its tissues and causing numerous dangerous diseases.
Some harmful components in cigarette smoke include:
Nicotine: Increases heart rate, forcing the heart to work harder, raises pulse and blood pressure, and is also addictive.
Tar: Contains many cancer-causing substances.
Carbon monoxide (CO): Reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of red blood cells, causing atherosclerosis, heart diseases, and strokes.
Nitrosamines, Benzene: Strong carcinogens. Benzene is commonly found in exhaust fumes and pesticides.
Ammonia: Used in growth stimulants and cleaning products.
Formaldehyde: Irritates the nose, throat, and eyes of smokers.

So, how do cigarettes affect the body? Why should you give up smoking?
1. Smoking Can Cause Cancer
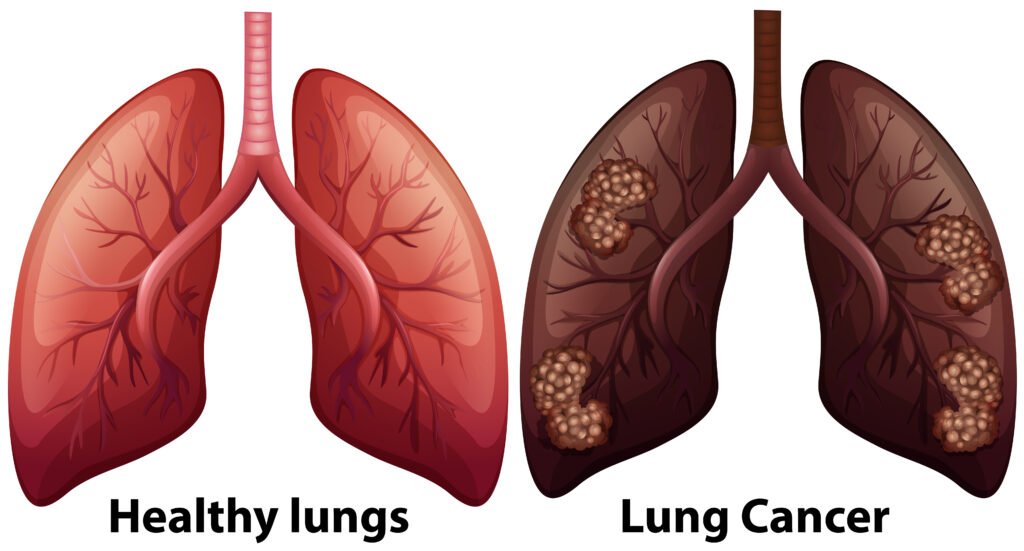
Smoking can cause cancer in nearly every organ of your body: lungs, bladder, blood, cervix, colon, esophagus, kidneys, throat, liver, pancreas, stomach, and more. When you smoke, carcinogenic chemicals from cigarettes enter your body through the alveoli in your lungs and spread throughout your body. These chemicals can cause mutations in your cells, leading to uncontrolled growth and cancer.
2. Damages and Destroys Lungs, Leading to Respiratory Failure
Smoking leads to the accumulation of significant amounts of chemicals in your lungs, respiratory system, and entire body. This buildup eventually clogs your lungs, causing respiratory issues and reduced lung function. This results in oxygen and fresh blood deficiency to different parts of the body, making you feel tired and short of breath. Studies show that smoking can lead to COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease), emphysema, chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, lung infections, asthma, and an increased risk of tuberculosis.
3. Increases Risk of Heart Disease and Stroke
Smokers are two to four times more likely to develop coronary artery disease and stroke than non-smokers. Chemicals in cigarette smoke affect the entire circulatory system and blood-forming organs, making blood vessel walls thicker and more prone to clotting. Additionally, it causes blood vessels to constrict and increases blood pressure, leading to plaque buildup and higher risk of cardiovascular diseases.
4. Reduces Sexual Function
Chemicals in cigarettes reduce blood flow, decrease sensation in the penis, cause cardiovascular diseases, and reduce stamina. All these factors together lead to reduced sexual performance, causing premature ejaculation. Nicotine is known to directly affect blood vessels supplying the penis, making it difficult to achieve and maintain an erection. Smoking also reduces sperm count, quality, motility, and causes sperm deformities, leading to infertility, miscarriages, and birth defects. Even passive smokers are at risk of erectile dysfunction.
5. Causes Teeth to Yellow
Cigarettes contain tar, a chemical that causes teeth to turn yellow. This tar is hard to remove with regular brushing and often leaves permanent stains on smokers’ teeth.
6.Causes Bad Breath
Smoking kills beneficial bacteria in the mouth and increases saliva production, leading to tartar formation. It also causes digestive issues, sore throats, and chemical buildup in the mouth (throat and stomach problems are major causes of bad breath besides poor oral hygiene).
7. Can Cause Blindness
Smoking greatly affects vision and can cause blindness. According to the CDC, smoking increases the risk of cataracts, age-related macular degeneration, optic nerve damage, and ultimately blindness.
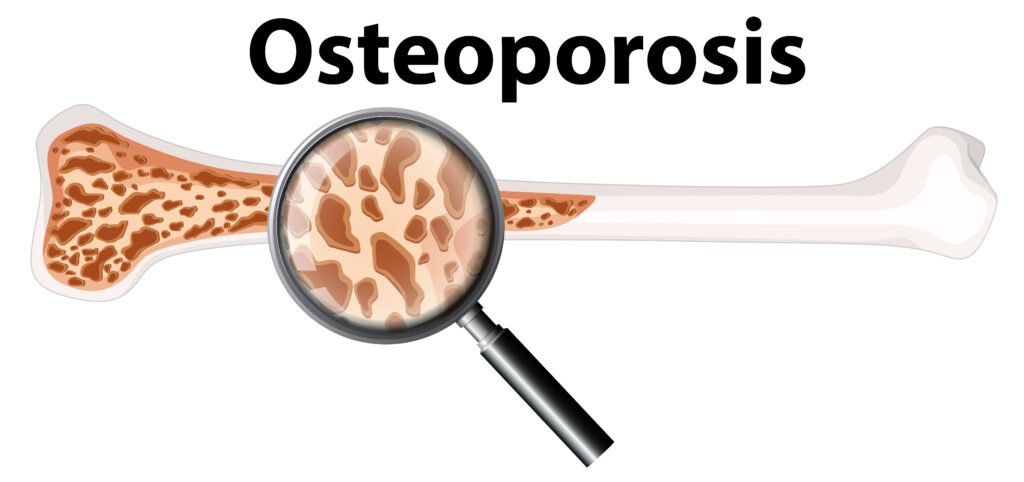
8. Weakens Bones
Many studies have found that smoking leads to reduced bone density due to increased calcium mobilization from bones to blood. Lower bone density can trigger early osteoporosis (especially in women, as smoking affects estrogen production), joint pain, and even tooth loss due to significant reduction in jawbone density. Osteoporosis also increases the risk of frequent fractures and slower healing.
9. Causes Wrinkles and Premature Aging
Smoking leads to wrinkles (especially around the eyes and mouth), age spots, puffy eyes, dull, dry, and lifeless skin. Chemicals in cigarettes cause capillaries under your skin to shrink, limiting blood flow to your skin. The lack of blood and oxygen makes your skin look dull and lifeless. Over time, this leads to permanent damage to connective fibers like elastin and collagen, which keep skin smooth and firm, causing permanent wrinkles and premature aging.
Regular cigarettes, electronic cigarettes, and any tobacco products contain many dangerous toxins. Now that you know how cigarettes affect the body, the best thing you can do for your health is to quit smoking completely. Don’t spend the rest of your life addicted to nicotine. Thousands of people give up this habit every year, and you should be one of them. It may not be easy, but you can do it!

